
Shashi Shankar
Apr 2, 2024
Time Travel
What is Time Travel?
Snowflake's Time Travel feature offers the capability to access historical data, allowing retrieval of data that has been changed or deleted within a defined period. This feature serves various purposes, including restoring data-related objects such as tables, schemas, and databases that may have been inadvertently or intentionally deleted, duplicating and backing up data, and analyzing data usage and manipulation over specified timeframes. Users can query data from the past that has since been updated or deleted, create clones of entire tables, schemas, and databases at or before specific points in the past, and restore dropped tables, schemas, and databases.

Limitations - Once the defined period of time has elapsed, the data is moved into Snowflake Fail-safe and these actions can no longer be performed.
Time Travel SQL Extensions
AT | BEFORE
TIMESTAMP -
OFFSET - time difference in seconds from the present time
STATEMENT Identifier (Query ID)
UNDROP
Data Retention Period
· The standard retention period is 1 day (24 hours) and is automatically enabled for all Snowflake accounts:
· Standard Edition – default is 0 days, that can be changed to 1 day
· Enterprise Edition –
o Transient object – 0 days
o Permanent databases, schemas and tables – 0 to 90 days
End of Retention Period
· Historical data is moved to Fail-Safe
· Query on historical data is no longer available
· Past objects can no longer be cloned
· Dropped past objects cannot be restored
· Specifying Data Retention Period – DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS, can be set by ACCOUNTADMIN role
o Can be used to explicitly override the default when creating a database, schema, and individual table
o Can be changed at any time
· MIN_DATA_RETENTION_PERIOD_IN_DAYS
o Can be set by ACCOUNTADMIN role
Enabling and Disabling Time Travel
· No tasks are required to enable Time Travel. It is automatically enabled with the standard, 1-day retention period.
· Time Travel cannot be disabled for an account.
· A user with the ACCOUNTADMIN role can set DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS to 0 at the account level
o Objects created subsequently will inherit it
o No impact on existing objects
· Time Travel can be disabled for individual databases, schemas, and tables by specifying DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS with a value of 0 for the object.
· To change the retention period for an object, use the appropriate ALTER <object> command
· Changing the retention period for your account or individual objects changes the value for all lower-level objects that do not have a retention period explicitly set
Querying Historical Data
· AT | BEFORE clause
· SELECT * FROM my_table AT(TIMESTAMP => 'Fri, 01 May 2015 16:20:00 -0700'::timestamp_tz);
· The following query selects historical data from a table as of 5 minutes ago: -
· SELECT FROM my_table AT(OFFSET => -605);
· The following query selects historical data from a table up to, but not including any changes made by the specified statement:
· SELECT * FROM my_table BEFORE(STATEMENT => '8e5d0caxxxxxxxxxxxc5726');

Cloning Historical Objects
CREATE TABLE restored_table CLONE my_table
AT(TIMESTAMP => 'Sat, 09 May 2015 01:01:00 +0300'::timestamp_tz);
CREATE SCHEMA restored_schema CLONE my_schema AT(OFFSET => -3600);
CREATE DATABASE restored_db CLONE my_db
BEFORE(STATEMENT => '8e5d0ca9-005e-44e6-b858-a8f5b37c5726');
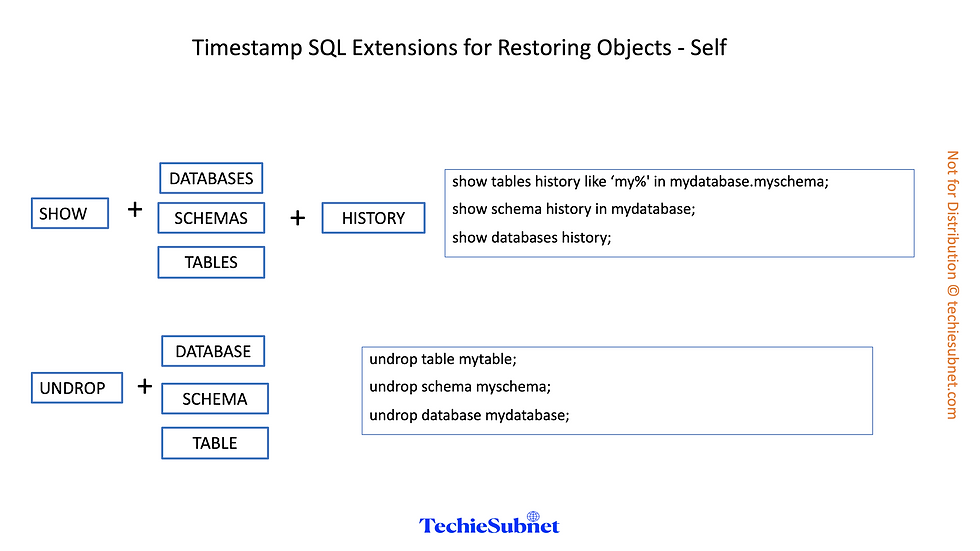
Listing Dropped Objects
SHOW TABLES HISTORY LIKE 'load%' IN mytestdb.myschema;
SHOW SCHEMAS HISTORY IN mytestdb;
SHOW DATABASES HISTORY;
Restoring Objects
UNDROP TABLE mytable;
UNDROP SCHEMA myschema;
UNDROP DATABASE mydatabase;
Access Control Requirements
· User must have OWNERSHIP privileges and CREATE privileges on the object type for the database or schema where the dropped object will be restored
· Restoring tables and schemas is only supported in the current schema or current database, even if a fully-qualified object name is specified.
